How Thick Should Interior, Exterior, and Load-Bearing Walls Be?
When designing or renovating a building, the thickness of walls plays a crucial role in stability, insulation, and space efficiency. The standard thickness for interior, exterior, and load-bearing walls depends on construction materials, building codes, and regional practices.
Here are the general guidelines:
- Interior walls (non-load-bearing): Usually 10–15 cm (4–6 inches) depending on materials such as drywall or brick.
- Exterior walls: Typically 20–40 cm (8–16 inches), influenced by insulation needs and climate conditions.
- Load-bearing walls: Generally 24–30 cm (9.5–12 inches) for brick or concrete structures, with reinforced framing in wooden constructions.
The exact thickness varies based on building regulations, insulation requirements, and construction methods. In digital planning software like Plan7Architect, users can select either metric or imperial measurements for accurate wall dimensioning.
Interior Wall Thickness
Standard Thickness of Non-Load-Bearing Interior Walls
Non-load-bearing interior walls primarily serve to divide rooms and do not support structural weight. Their thickness depends on the chosen construction material:
| Material | Standard Thickness |
|---|---|
| Drywall (plasterboard on frame) | 10 cm / 4 in |
| Brick (single layer) | 12–15 cm / 5–6 in |
| Concrete | 10–15 cm / 4–6 in |
Drywall partitions are commonly used in residential and office spaces due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Brick or concrete interior walls provide better sound insulation and durability.
Factors Influencing Interior Wall Thickness
- Acoustic insulation: Thicker walls or double layers of drywall enhance soundproofing, essential in apartments or office buildings.
- Fire resistance: Brick and concrete interior walls offer better fire resistance compared to drywall.
- Plumbing and electrical installations: Walls housing pipes or wiring often require increased thickness to accommodate these systems.
Tip: If planning a home with integrated plumbing in walls, consider a thickness of at least 15 cm (6 inches) to prevent structural weaknesses and noise transmission from pipes.
Exterior Wall Thickness
Common Exterior Wall Thickness by Material
Exterior walls must provide thermal insulation, weather resistance, and structural support. The required thickness depends on the material used:
| Material | Typical Thickness |
|---|---|
| Wood Frame Construction | 20–30 cm / 8–12 in |
| Brick (with insulation) | 24–36 cm / 9.5–14 in |
| Reinforced Concrete | 25–40 cm / 10–16 in |
Key Factors Affecting Exterior Wall Thickness
- Climate conditions: In cold regions, thicker walls with added insulation (e.g., 30–40 cm / 12–16 inches) help improve energy efficiency.
- Energy efficiency: Passive houses and energy-efficient homes require increased insulation layers, which can add 5–15 cm (2–6 inches) to the total thickness.
- Structural integrity: Multi-story buildings often require reinforced walls to support the upper levels, increasing wall dimensions accordingly.
Tip: For optimal insulation, ensure the exterior wall includes an insulated core between the structural material, such as brick with an insulation layer or a wood frame with foam or fiberglass insulation.


Load-Bearing Wall Thickness
Minimum Requirements for Load-Bearing Walls
Load-bearing walls provide essential structural support and must comply with building regulations regarding their thickness.
| Construction Type | Minimum Thickness |
|---|---|
| Brick or Concrete | 24–30 cm / 9.5–12 in |
| Wooden Frame (with reinforcements) | Structural beams required |
| Reinforced Concrete | 25–40 cm / 10–16 in |
How to Identify Load-Bearing Walls?
- Position: Typically located at the center of the building or along the perimeter.
- Thickness: Load-bearing walls are usually thicker than partition walls.
- Structural dependencies: Walls supporting beams, upper floors, or roof structures cannot be removed without professional evaluation.
Special Considerations & Regional Differences
Building codes determine minimum wall thicknesses, insulation requirements, and fire resistance standards. While standard thickness values remain similar across regions, local regulations may impose stricter guidelines based on seismic activity, weather conditions, and energy efficiency goals.
In software like Plan7Architect, users can easily adjust wall thicknesses according to building standards and seamlessly switch between metric and imperial measurements.
Plan and Design Professional Floor Plans with Plan7Architect
With Plan7Architect, you can easily plan and design precise interior, exterior, and load-bearing walls, ensuring they meet structural requirements and insulation standards. Whether you’re working with brick, concrete, wood, or drywall, the software allows you to set the correct wall thickness and adjust dimensions with both European and American measurement units.
Create professional floor plans with accurate wall layouts, insulation layers, and structural elements, all in 2D and 3D views. The software is user-friendly and perfect for homeowners, architects, and builders who need detailed, high-quality plans.
To give you full confidence in your purchase, we offer a 14-day cancellation policy—you can easily withdraw your purchase via email if the software doesn’t meet your expectations.
Plan your project with Plan7Architect
Plan7Architect Pro 5 for $109.99
You don’t need any prior experience because the software has been specifically designed for beginners. The planning process is carried out in 5 simple steps:
1. Draw Walls


2. Windows & Doors


3. Floors & Roof


4. Textures & 3D Objects


5. Plan for the Building Permit



6. Export the Floor Plan as a 3D Model for Twinmotion
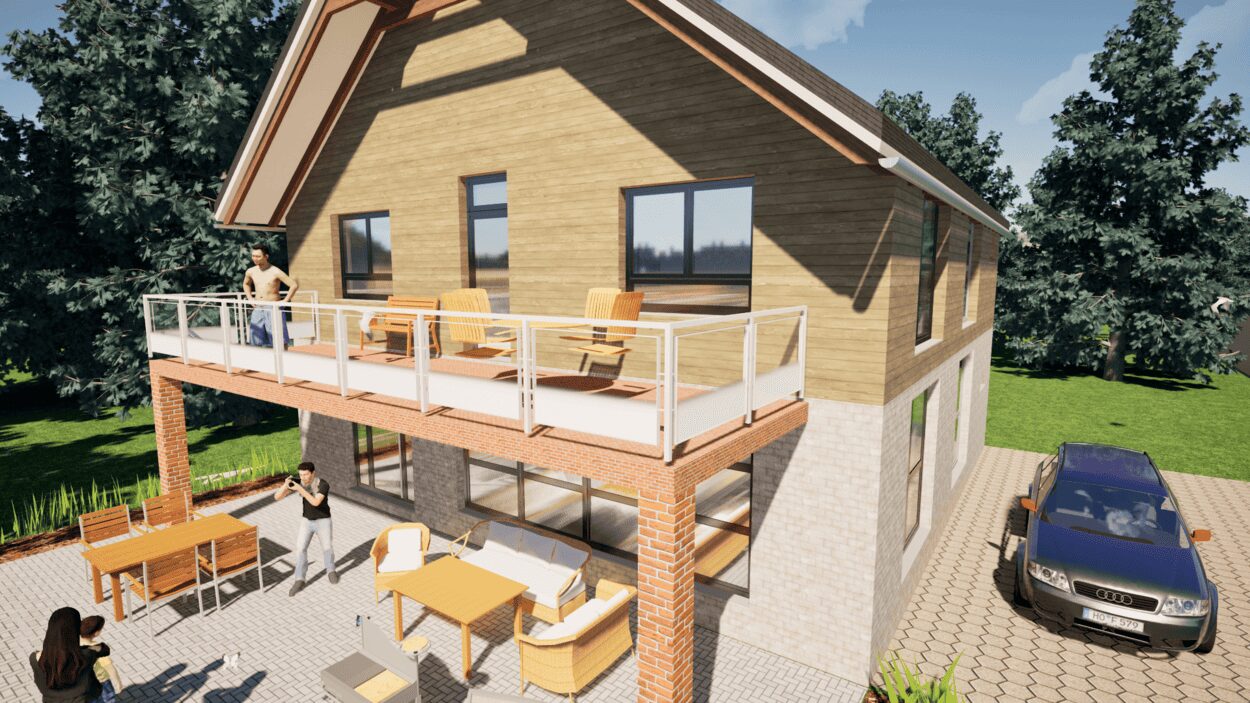



- – Compliant with international construction standards
- – Usable on 3 PCs simultaneously
- – Option for consultation with an architect
- – Comprehensive user manual
- – Regular updates
- – Video tutorials
- – Millions of 3D objects available