What Is a Modular House? (Definition)
A modular house is a prefabricated home built in sections—called modules—in a factory setting, then delivered and assembled on a permanent foundation at the final location. These modules are constructed using the same materials and building techniques as traditional homes. Once assembled, a modular home is virtually indistinguishable from a conventionally built house in terms of appearance, stability, and durability.
Unlike mobile homes, modular houses are not movable once installed. They are classified as permanent structures and must comply with the local building codes in the area where they’re placed. Whether you are planning to build in Europe or North America, the modular home will be designed to meet local safety, insulation, and structural standards. In most cases, the modules are craned into place and secured together on-site within a few days.
Key Advantages of Modular Homes
Faster Construction Times
One of the most noticeable benefits of modular construction is speed. Because modules are manufactured in parallel with site preparation, the total construction time is significantly reduced. While a conventional build might take 9 to 12 months, a modular home can often be completed in 3 to 5 months, depending on complexity.
This makes modular homes ideal for anyone facing a tight schedule or needing to move into a home quickly. Delays due to weather are also minimized, since most of the building takes place indoors at the factory.
Cost Efficiency
Modular homes are generally more affordable than site-built homes of the same size and standard. This is due to several factors:
-
Less labor time needed on-site
-
Reduced material waste during factory production
-
Minimal weather-related delays
-
Predefined design options that lower customization costs
| Expense Factor | Modular Home | Traditional Home |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Weather Delays | Rare | Frequent |
| Material Waste | Reduced | High |
| Time to Completion | 3–5 months | 9–12 months |
High Quality Control
Each module is built under strict factory controls, which often results in higher and more consistent quality than homes built entirely on-site. Every step of the manufacturing process is monitored and inspected, reducing the risk of defects and ensuring compliance with building standards.
Also, because the modules are constructed indoors, they are protected from moisture damage during the build process—something that often causes issues in traditional builds exposed to the weather.
Flexible Design Options
Despite some limits, modular homes offer a surprising amount of flexibility. You can choose from a variety of layouts, finishes, and architectural styles. Many manufacturers offer design libraries that include both modern and classic floor plans.
It’s also possible to extend a modular home later on. For example, you can plan your house to include space for an additional module in the future—ideal for growing families or changing needs.
Tip:
If you plan your modular house with software like Plan7Architect, you can easily simulate future expansions and check how additional modules will fit in both 2D and 3D views.
Eco-Friendly Building
Modular homes are often more sustainable than conventional houses. The controlled factory environment minimizes material waste and allows for better recycling practices. In addition, many manufacturers offer environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient upgrades.
Advantages include:
-
Reduced carbon footprint during construction
-
Lower energy usage due to improved insulation
-
Option to add solar panels or green roofs


Disadvantages and Challenges of Modular Homes
Limited Customization (Compared to Traditional Builds)
While modular homes are available in a range of designs, extreme customizations can be difficult or costly. This is because modules are built to standardized specifications. If you require highly unique layouts or unusual architectural features, a modular home might not be the best fit.
Once the factory process begins, making changes to the design is either impossible or very expensive. Planning ahead is critical.
Transportation and Crane Logistics
The modules are large and heavy. Transporting them requires trucks with permits, and installing them usually involves a crane. This can pose challenges if your property is located in a remote area, has poor access roads, or has steep terrain.
You should also check local transport regulations and site accessibility before deciding on a modular approach.
Financing and Insurance Can Differ
In some regions, banks and insurers treat modular homes differently from traditional ones. Although the situation is improving, certain institutions may still have unfamiliar or outdated policies.
You might need to consult with lenders and insurance companies beforehand to make sure they support modular construction.
Zoning Restrictions in Certain Regions
Local zoning laws may limit or prohibit modular construction, especially in older neighborhoods or historic districts. Some municipalities may require additional documentation or approval for prefabricated buildings.
Before purchasing land or signing a building contract, it is important to verify that modular homes are allowed in your area.
Typical Features and Construction Details
How Modular Homes Are Built
The process starts with designing your home layout. Once approved, each module is built in a controlled factory environment, complete with insulation, wiring, plumbing, and wall finishes. After construction, the modules are transported to your site and assembled on a prepared foundation.
Depending on the complexity, the onsite assembly phase can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks. Finishing work like roofing seams, interior joints, and landscaping is then completed.
Size, Layout, and Style Options
Modular homes can be single-story cottages, spacious two-story family homes, or even minimalist studios. You can combine multiple modules in different configurations—L-shape, U-shape, or stacked vertically.
Layout flexibility includes:
-
Open-concept kitchens and living rooms
-
En-suite bathrooms
-
Home offices and guest rooms
-
Garage or carport options
Modular homes are available in both metric and imperial units. With Plan7Architect, you can freely switch between meters and feet to match your local standard during the design phase.


Materials and Insulation Standards
Most modular homes are made with the same materials as conventional buildings: timber framing, OSB or drywall, roofing shingles, and proper insulation. High-performance windows and doors are also standard.
Depending on your region, the insulation values (R-values or U-values) will be adapted to comply with local energy efficiency codes.
Compliance With Local Building Codes
A properly designed modular home meets the same regulations as any other house. That includes fire safety, structural integrity, insulation standards, and earthquake or storm resilience, where required.
The manufacturer must ensure the design is code-compliant for the destination, whether it’s the United States, Canada, the UK, Germany, or another country.
Is a Modular Home Right for You?
Ideal For…
-
Homeowners who want to move in quickly
-
Budget-conscious individuals or families
-
Environmentally minded buyers
-
Remote builds where local labor is limited
-
Those open to pre-designed layouts
Less Ideal If…
-
You require a fully custom, architect-designed home
-
Your land has difficult access or zoning limitations
-
You need extreme layout flexibility
-
Your financing depends on traditional construction terms
Planning a Modular Home with Software
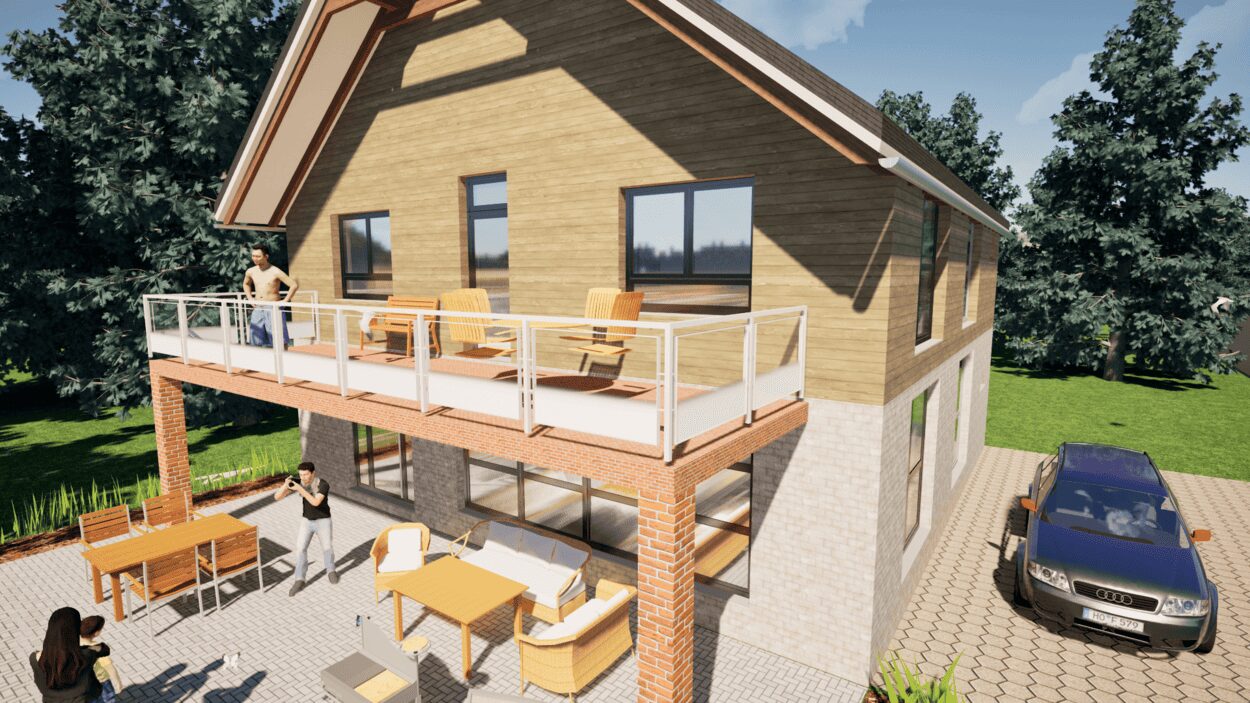
To visualize and plan your modular house accurately, software like Plan7Architect is extremely helpful. It lets you design and simulate floor plans in 2D and 3D, choose room layouts, and adjust wall thicknesses, ceiling heights, and roof structures.
You can set measurements in either metric (meters, centimeters) or imperial (feet, inches) depending on your regional standard. The software supports professional-level planning while remaining intuitive enough for private builders.
Features that help with modular planning:
-
Layer-based planning for each module
-
Real-time 3D walkthroughs
-
Roof, terrace, and staircase customization
-
Export-ready plans for permit submission
Conclusion – Modular Homes in a Nutshell
Modular homes offer a modern, practical alternative to conventional construction. They are faster, more affordable, and often more sustainable, making them an excellent choice for private homeowners and developers alike. With proper planning and the right tools, you can create a modular home that matches your needs, budget, and lifestyle.
Plan your project with Plan7Architect
Plan7Architect Pro 5 for $99.99
You don’t need any prior experience because the software has been specifically designed for beginners. The planning process is carried out in 5 simple steps:
1. Draw Walls


2. Windows & Doors
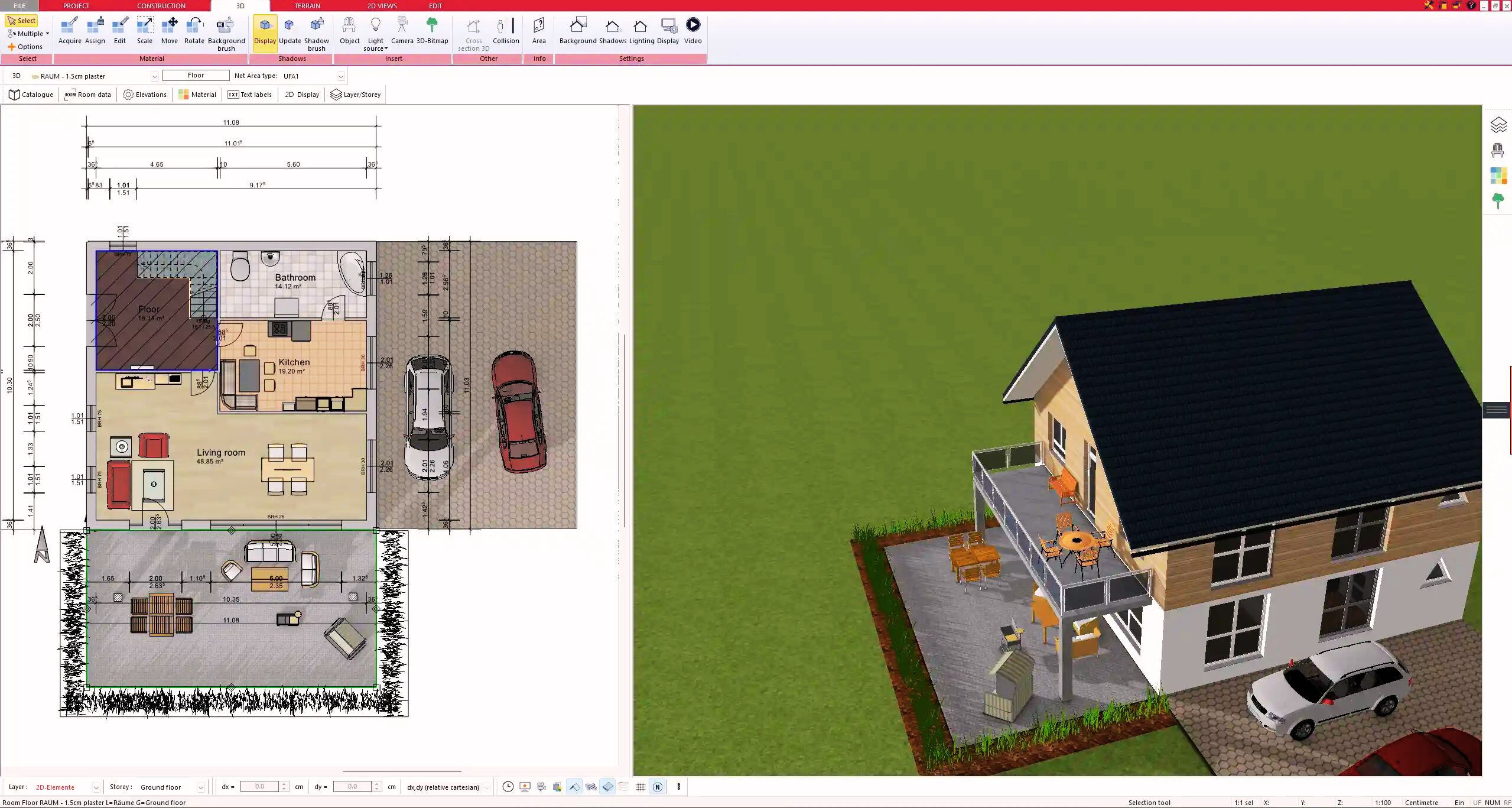


3. Floors & Roof
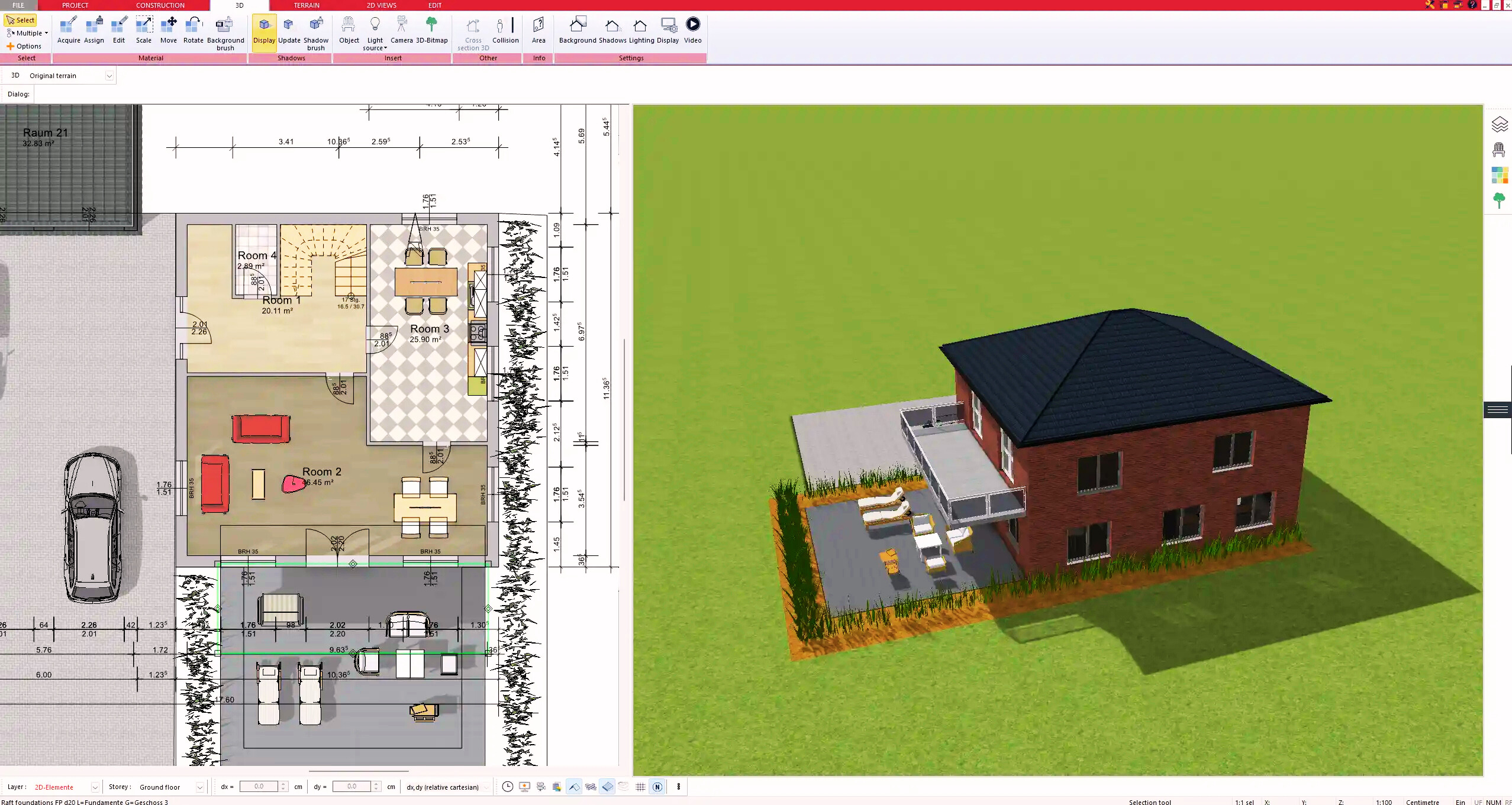


4. Textures & 3D Objects
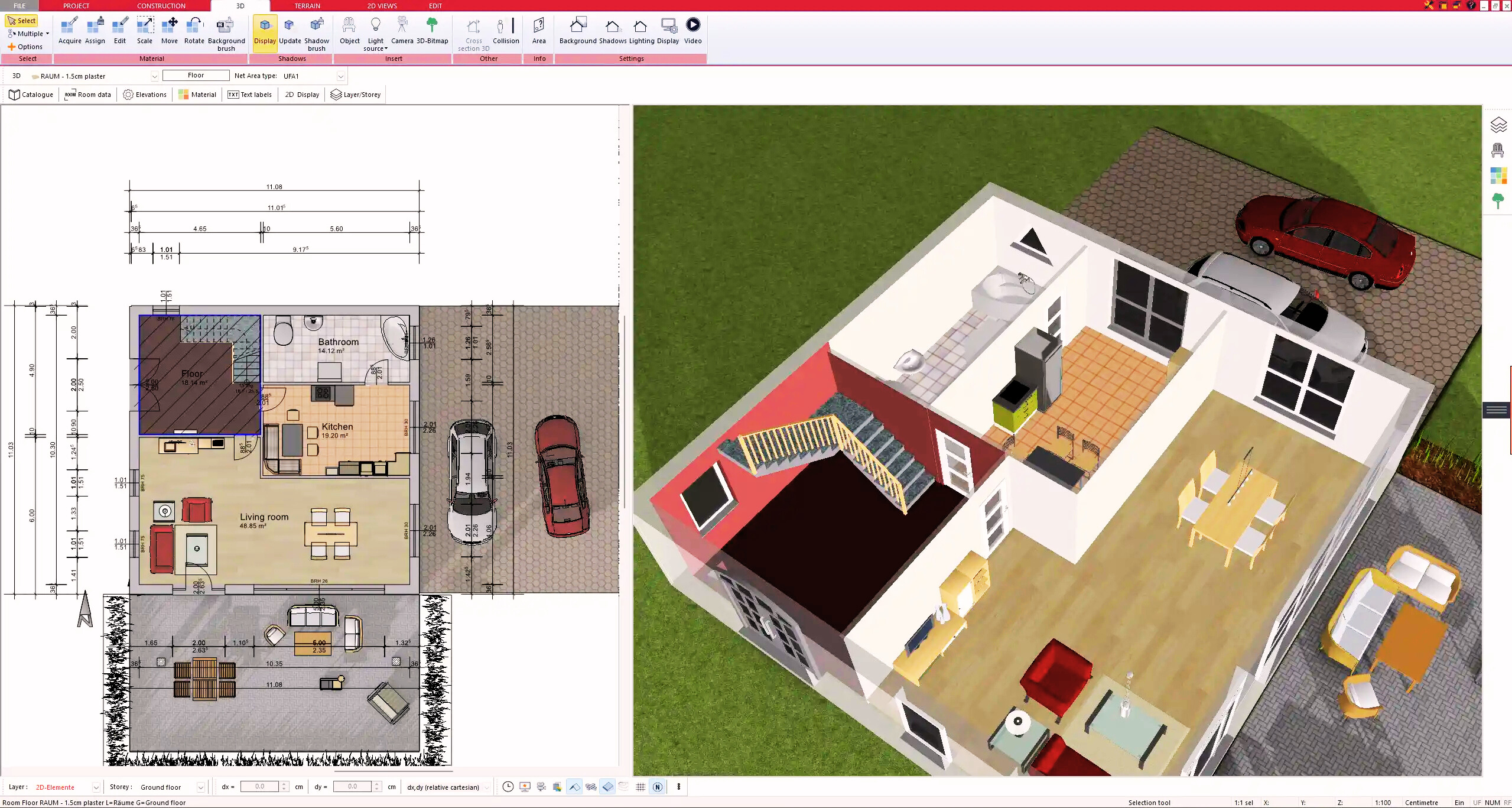


5. Plan for the Building Permit



6. Export the Floor Plan as a 3D Model for Twinmotion



- – Compliant with international construction standards
- – Usable on 3 PCs simultaneously
- – Option for consultation with an architect
- – Comprehensive user manual
- – Regular updates
- – Video tutorials
- – Millions of 3D objects available