What Is a Prefab House? (Definition)
A prefab house, short for “prefabricated house”, is a home that is manufactured off-site in advance, usually in standard sections that can be easily shipped and assembled. Unlike traditional houses built entirely on-site, prefab homes are constructed in a factory-controlled environment and then transported to the final building location for assembly.
The core idea behind prefab housing is efficiency — both in time and cost. Most of the building components, such as walls, floors, roofs, and even full rooms, are pre-built in modules. These modules are then joined together at the site.
There are several types of prefab homes:
-
Modular homes: Built in multiple factory-produced sections, then assembled on-site like large building blocks.
-
Panelized homes: Delivered as wall panels, roof trusses, and floors that are assembled at the site.
-
Pre-cut homes: Also known as kit homes, where materials are pre-cut to size but assembled entirely on-site.
-
Manufactured homes: Fully constructed in the factory and transported to the site, often built on a steel frame.
Prefab construction is widely used in many countries and is becoming increasingly popular due to its speed and precision. Many modern prefab homes are indistinguishable from traditionally built homes in terms of design and quality.
Advantages of a Prefab House
Faster Construction Time
Prefab houses are significantly quicker to build than traditional homes. Since the components are manufactured indoors in parallel with site preparation, there are no delays due to weather or scheduling conflicts. In my own experience, I’ve seen projects completed in a matter of weeks that would otherwise take months.
On-site assembly is often completed in a few days, especially for modular homes. This makes prefab an excellent option for anyone needing fast occupancy.
Cost Efficiency
Prefab homes tend to be more cost-effective because the building process is optimized for scale and consistency. Labor costs are reduced, as less time is needed on-site, and material waste is minimized thanks to controlled production in the factory.
In addition, costs are more predictable. Since most of the structure is built in advance, unexpected expenses are less likely during construction.
Cost-saving advantages include:
-
Fewer delays
-
Lower risk of mistakes
-
Fixed design packages
-
Reduced need for contractors on-site
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Modern prefab homes are designed with sustainability in mind. Since components are produced in a factory, insulation, seals, and energy systems can be installed more precisely, reducing energy loss.
Many prefab models come pre-equipped with:
-
Triple-glazed windows
-
High-grade insulation
-
Air-tight building envelopes
-
Compatibility with renewable energy (e.g., solar panels, heat pumps)
This not only lowers monthly energy costs but also supports an eco-friendly lifestyle from day one.
Quality Control
In a traditional construction environment, quality can vary depending on weather, contractor skill, and material conditions. In a prefab factory setting, these variables are minimized.
Manufacturing under controlled conditions leads to:
-
Consistent precision in measurements and cuts
-
Better material storage and handling
-
Thorough inspections before delivery
I’ve personally seen prefab homes outperform traditional buildings in both tightness and thermal performance.


Disadvantages of a Prefab House
Limited Customization Options
While some manufacturers offer a range of styles and layouts, the flexibility is often less than in custom-built homes. Adding unique architectural features, altering room dimensions, or integrating special materials can increase costs and delay delivery.
If you want a fully customized home with unconventional shapes or finishes, prefab might not offer the creative freedom you’re looking for.
Transportation and Access Challenges
Delivering large modular parts to your building site can be a logistical challenge. The road to the location must be wide and stable enough to handle oversized transport vehicles.
In rural areas or mountainous terrain, this can add significant complexity. Permits for transportation, cranes for unloading, or road closures may be necessary.
Planning and Building Code Limitations
Depending on your country or region, prefab houses may be subject to specific zoning or permit restrictions. In some places, local building codes were written with only traditional construction in mind, requiring special approval or adaptation.
Before committing to a prefab solution, it’s important to check:
-
Whether local codes accept modular designs
-
Foundation requirements
-
Utility connection regulations
In many cases, these issues are easy to resolve — but it’s something to prepare for early.
Key Features of a Modern Prefab House
Modular Structure and Layout
Modern prefab homes can be designed as single units or combined into larger multi-module structures. This modular approach makes it easy to scale the house based on your space or budget.
A typical layout might include:
| Area | Module Type | Delivered As |
|---|---|---|
| Living Room | Full module | Fully enclosed |
| Kitchen | Full module | With pre-installed fixtures |
| Bathroom | Wet module | Pre-plumbed |
| Bedrooms | Panel modules | Assembled on site |
Each module is designed for quick connection and easy integration with plumbing, electricity, and HVAC systems.
Structural Materials
Prefab homes use a variety of materials depending on climate, budget, and regional standards. Common materials include:
-
Wood frame panels – lightweight, good insulation
-
Steel frames – high strength, termite-resistant
-
Concrete panels – durable and fire-resistant
Each material has its advantages. In colder regions, wood panels with advanced insulation are common. In tropical areas, concrete is often preferred due to its durability.


Flexible Interior Design
Contrary to older beliefs, modern prefab homes do not have to look “boxy” or simple. Many now feature open-concept living areas, high ceilings, and integrated smart-home systems.
Features I’ve personally found useful:
-
Moveable partition walls
-
Floor-to-ceiling windows
-
Built-in storage solutions
-
Underfloor heating options
Even though customization is more limited than with traditional building, the design still offers impressive flexibility.
International Relevance
Prefab houses are being built all over the world — from the United States and Canada to Germany, Japan, and Australia. In each region, the materials, insulation, and layout can be adapted to local climate and regulations.
When it comes to planning, using software that supports both European (meters) and American (feet/inches) units is essential. With Plan7Architect, you can plan and switch between unit systems at any time, making it easy to work across international standards or with global teams.
For Whom Is a Prefab House Suitable?
Prefab homes are a great choice for:
-
First-time homeowners looking for an affordable entry into the housing market
-
People needing a home quickly after a relocation or disaster
-
Remote builders who want to avoid the logistical burden of on-site construction
-
Eco-conscious individuals seeking sustainable building options
-
Investors looking to build rental properties or holiday homes at scale
If you’re someone who values speed, cost transparency, and energy efficiency, prefab could be an ideal solution.
Common Misconceptions About Prefab Houses
There are still outdated ideas about prefab housing that need to be addressed:
-
“Prefab equals low quality” – In reality, many prefab homes exceed traditional building standards in insulation, airtightness, and structural stability.
-
“They all look the same” – Modern prefab houses come in many styles, including minimalist, rustic, Scandinavian, and ultra-modern.
-
“Prefab means mobile home” – While manufactured/mobile homes fall under the prefab category, modular homes are fully compliant with local building codes and are placed on permanent foundations.
Understanding these differences helps you make a better-informed decision when planning your home.
Planning a Prefab House with Software
Planning a prefab home digitally helps you avoid mistakes and visualize the result long before construction begins.
With Plan7Architect, you can:
-
Design the entire floor plan in 2D and instantly switch to 3D
-
Position rooms, modules, and utilities exactly as needed
-
Customize wall thickness, door sizes, and roof angles
-
Work in both metric and imperial units, depending on your country or construction team
-
Export your plans for submission to local authorities or builders
If you’re planning a modular home, the software also allows you to group rooms into building blocks that mimic the prefab assembly process.
Tip:
Use layers in Plan7Architect to separate modules, electrical layouts, or plumbing lines. This makes your plan easier to present to contractors or local officials.
Plan your project with Plan7Architect
Plan7Architect Pro 5 for $99.99
You don’t need any prior experience because the software has been specifically designed for beginners. The planning process is carried out in 5 simple steps:
1. Draw Walls


2. Windows & Doors


3. Floors & Roof


4. Textures & 3D Objects


5. Plan for the Building Permit



6. Export the Floor Plan as a 3D Model for Twinmotion
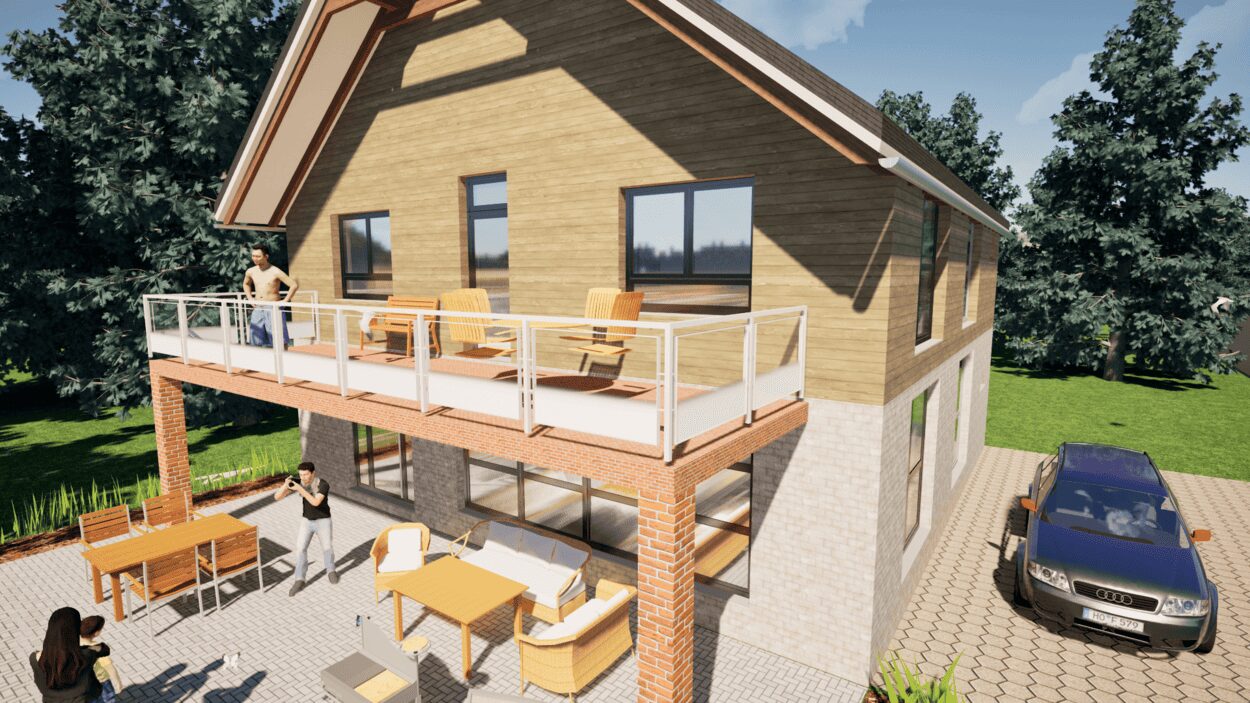



- – Compliant with international construction standards
- – Usable on 3 PCs simultaneously
- – Option for consultation with an architect
- – Comprehensive user manual
- – Regular updates
- – Video tutorials
- – Millions of 3D objects available